Leprosy or leprosy is a chronic bacterial infection that attacks skin tissue, peripheral nerves and the respiratory tract. Leprosy or leprosy is also known as Hansen’s disease or Morbus Hansen.
Leprosy or leprosy can be characterized by weakness or numbness in the legs and feet, followed by the appearance of lesions on the skin. This disease, which is caused by a bacterial infection, can spread through splashes of saliva or phlegm that come out when the sufferer coughs or sneezes.
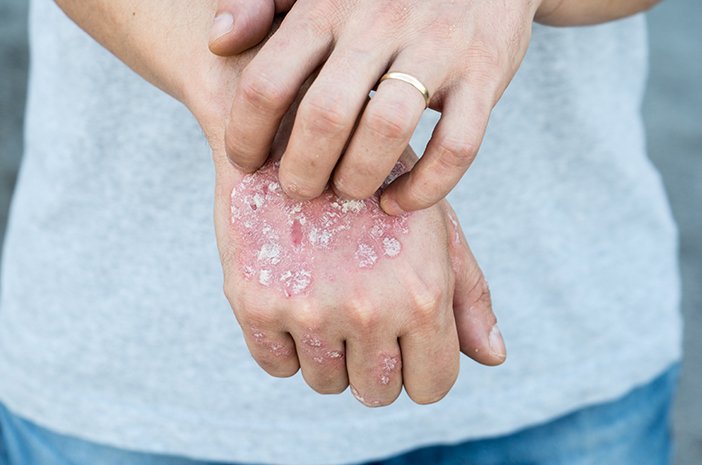
The incidence of leprosy in Indonesia is among the highest. Based on WHO data for 2020, the number of leprosy cases in Indonesia is ranked third largest in the world, namely 8%. Apart from that, 9.14% of the total new cases of leprosy occurred in children.
Leprosy is generally treatable and rarely causes death. However, this disease has the risk of causing disability. As a result, leprosy sufferers are at risk of experiencing discrimination which can have an impact on their psychological condition.
Causes of Leprosy
Leprosy or leprosy is caused by infection with the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae. This bacteria can be transmitted from one person to another through fluid splashes from the respiratory tract (droplets), namely saliva or phlegm, which comes out when coughing or sneezing.
A person can contract leprosy if they are exposed to droplets from the sufferer continuously for a long time. In other words, the bacteria that cause leprosy cannot be transmitted to other people easily. Apart from that, these bacteria also take a long time to reproduce in the sufferer’s body.
It should be noted that leprosy can be transmitted if contact occurs for a long time. Leprosy will not be transmitted just by shaking hands, sitting with, or having sexual relations with the sufferer. Leprosy is also not transmitted from mother to fetus.
Apart from the causes above, there are several other factors that can increase a person’s risk of developing leprosy, including:
-
- Coming into contact with animals that spread leprosy bacteria, such as armadillos
- Living in or visiting a leprosy endemic area
- Have an immune system disorder
Symptoms of Leprosy
Symptoms of leprosy are not obvious at first and usually develop slowly. In fact, in some cases, symptoms of leprosy can only be seen after leprosy bacteria have multiplied in the sufferer’s body for 20 years or more.
Some of the symptoms of leprosy that sufferers can feel are:
- The skin becomes numb, including losing the ability to sense temperature, touch, pressure, or pain
- Skin does not sweat
- Skin feels stiff and drypainless ulcers on the soles of the feet
- painless sores on the soles of the feet
- Swelling or lumps on the face and ears
- Spots that appear pale and lighter in color than the surrounding skin
- Enlarged nerves, usually in the elbows and knees
- Muscle weakness, especially in the legs and arms
To diagnose leprosy, the doctor will ask about the symptoms experienced, then examine the patient’s skin. The doctor will check whether there are lesions on the skin as symptoms of leprosy or not. Leprosy lesions on the skin are usually pale or red (hypopigmentation) and accompanied by numbness.To determine whether the patient suffers from leprosy, the doctor will take a skin sample by scraping it (skin smear). This skin sample will then be analyzed in the laboratory to check for the presence of Mycobacterium leprae bacteria. The analysis method includes examination of acid-fast bacteria (BTA).
In leprosy endemic areas, a person can be diagnosed with leprosy even if a skin scraping test shows negative results. This refers to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of leprosy, namely:
Paucibacillary, namely there are skin lesions even though the results of the skin scraping (smear) test are negative
Multibacillary, that is, there are skin lesions with positive skin scraping (smear) test resultsLeprosy Treatment
The main method for treating leprosy or leprosy is with antibiotics. Leprosy sufferers will be given a combination of several types of antibiotics for 1-2 years. The type, dose and duration of antibiotic use will be determined based on the type of leprosy suffered.
Examples of antibiotics used to treat leprosy are:
- Rifampicin
- Dapsone
- Clofazimine
- Minocycline
- Ofloxacin
In Indonesia, leprosy treatment is generally carried out using the MDT method or multidrug therapy, namely treatment that combines two or more antibiotics.
After treatment with antibiotics, surgery will generally be performed as further treatment. Operations for leprosy sufferers aim to:
- Normalizes damaged nerve function
- Correct deformed body shape
- Restores body function
Leprosy Prevention
Until now, there is no vaccine to prevent leprosy. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are the best efforts to prevent complications and transmission of leprosy. Apart from that, avoiding contact with animals that carry leprosy bacteria is also important to prevent leprosy.
An integrated movement to provide information about leprosy to the public, especially in endemic areas, is an important step so that sufferers are willing to check themselves and receive treatment.
It is also hoped that providing this information can eliminate the negative stigma about leprosy and discrimination against leprosy sufferers.


No Responses